Structured Cabling vs Conventional Point-to-Point Cabling
What is structured cabling?
Structured Cabling… is defined as building or campus telecommunications cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements (structured).
A properly designed and installed structured cabling system provides a cabling infrastructure that delivers predictable performance as well as has the flexibility to accommodate moves, adds and changes; maximizes system availability, provides redundancy; and future proofs the usability of the cabling system.
– as defined on CABLExpress.com cabling glossary
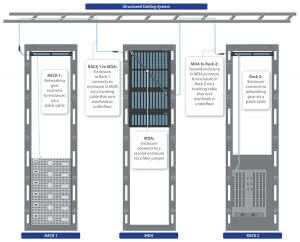
Structured Cabling Solution
Point-to-Point Cabling (Conventional Structured Cabling System)
What is the benefit of structured cabling system
What Are the Benefits of Structured Cabling?
Once again, organization is the key word here. With an organized structured cabling system the benefits are:
MAC’s are much quicker due to the fact that they are done in the MDA versus running long patch cords from equipment racks.
Potential for downtime is reduced as potential for human error is drastically reduced due to this organization.
Time savings: cable and port tracing becomes a much easier job with a structured cabling system.
Aesthetics: Never underestimate the looks! A structured cabling system will look much cleaner than a point to point method. Since the changes are done in the MDA versus at the hardware, the hardware can be cabled up and not touched in most instances. This allows the cabling in front of the switch to remain aesthetically pleasing.
What are Risk staying with conventional structured cabling system
Downtime!
With an unorganized messy cabling infrastructure, mistakes are commonly made. Incorrect ports are unplugged. Even worse is the messy cabling that gets in the way. Trying to remove a single cable from a large tangled mess can cause stress on the other cables. This stress can lead to network and channel errors in the hardware that are very difficult to trace.
Airflow: If a point to point method is used, the front and potentially the sides of the switch are congested with cabling bulk. This impedes the airflow that the switch needs to operate. This also translates to underfloor cooling; cabling congestion in this space hinders the airflow of the CRAC unit and can cause cooling issues.